Real-name ticketing, also known as 实名制 (shímíngzhì) in Chinese, is a system where individuals must provide valid government-issued identification (e.g., ID card, passport) to purchase tickets, and the ticket is linked to their personal information. This practice ensures that the ticket holder’s idenRead more
Core Mechanism
- Identity Verification:
When purchasing tickets (online or in-person), users must submit their full name, ID number, and sometimes biometric data (e.g., facial recognition). For example, Shanghai Disney Resort requires guests to use their ID cards or passports to buy tickets, and the same document must be presented for entry 16. - Non-Transferable Tickets:
Once purchased, tickets cannot be resold or transferred to another person. This prevents scalping and ensures only the registered user can use the ticket. - Data Collection:
Ticket sellers store personal information to comply with regulations and monitor usage. For instance, China’s railway system mandates that all passengers provide ID details, which are stored securely 910.
Key Applications
-
- Railways: In China, all train tickets are 实名制,with ID checks at stations. Even temporary ID cards or passports are accepted for verification 913.
- Aviation: International airlines like Air China require passengers to provide ID details that match their boarding passes 17.
- Ferry Services: The Qiongzhou Strait ferry in Hainan Province implemented real-name ticketing in 2017, requiring passengers to present IDs for both purchase and boarding 4.
-
- Concerts and Sports: Large-scale events in China, such as the 2023 National Day celebrations, enforce real-name ticketing to prevent fraud. Each ID can buy only one ticket, and entry requires a physical ID check 14.
- Theme Parks: Shanghai Disney Resort introduced real-name policies in 2024, where tickets are tied to the purchaser’s ID and cannot be altered 16.
-
- Scenic Spots: Attractions like Ningxia’s Xixia Tombs and Hainan’s Baishiling Scenic Area use real-name systems to manage visitor flows and protect cultural heritage 38.
Benefits
- Security: Real-name systems help authorities track individuals in emergencies (e.g., pandemics or criminal investigations). For example, during COVID-19, China used ticket data to trace contacts 3.
- Anti-Scalping: By linking tickets to IDs, resellers struggle to profit from bulk purchases. In 2023, China’s Ministry of Culture and Tourism reported a 60% drop in scalping cases at concerts after enforcing 实名制 14.
- Efficiency: Electronic ticketing and ID verification reduce queues. Hubei Province’s bus stations now allow passengers to board with a QR code or ID scan 7.
Challenges and Concerns
- Privacy Risks: Storing personal data raises concerns about leaks. For example, discarded train tickets with partial ID numbers could expose sensitive information 12. Companies like Piaoniu address this by encrypting data and limiting access 19.
- Inconvenience for Users: Travelers must carry physical IDs, and international visitors may face language barriers. Some countries, like Japan, allow 假名 (pseudonyms) for hotel check-ins, contrasting with China’s strict policies 5.
- Technical Hurdles: Systems must handle large volumes. China’s railway network processes over 1 million real-name transactions daily, requiring robust infrastructure 9.
Global Variations
- China: Real-name ticketing is widespread and legally mandated for transportation, events, and even phone SIM cards 59.
- United States: While TSA requires ID checks for flights, tickets are not linked to IDs. However, the “Real ID” program (effective 2023) mandates stricter ID verification for domestic travel 2.
- Europe: Some countries (e.g., Germany) require ID for train tickets, but enforcement varies. Most EU nations prioritize privacy, limiting data collection 5.










What is real-name ticketing?
Real-name ticketing, also known as 实名制 (shímíngzhì) in Chinese, is a system where individuals must provide valid government-issued identification (e.g., ID card, passport) to purchase tickets, and the ticket is linked to their personal information. This practice ensures that the ticket holder’s idenRead more
Core Mechanism
When purchasing tickets (online or in-person), users must submit their full name, ID number, and sometimes biometric data (e.g., facial recognition). For example, Shanghai Disney Resort requires guests to use their ID cards or passports to buy tickets, and the same document must be presented for entry 16.
Once purchased, tickets cannot be resold or transferred to another person. This prevents scalping and ensures only the registered user can use the ticket.
Ticket sellers store personal information to comply with regulations and monitor usage. For instance, China’s railway system mandates that all passengers provide ID details, which are stored securely 910.
Key Applications
Benefits
Challenges and Concerns
Global Variations
Conclusion
How do you view Speed's trip to China?
Speed's trip to China is a remarkable cultural exchange event with multiple positive aspects, which can be analyzed from the following perspectives: Breaking Stereotypes Regarding Technological Development: Through his live - streams, Speed showed the advanced aspects of China's technology anRead more
Which sites should tourists visit if they want to experience traditional Chinese culture?
Here are some sites that tourists can visit to experience traditional Chinese culture: Ancient Capitals Beijing Forbidden City:It is the imperial palace of the Ming and Qing dynasties, showcasing magnificent royal architecture, precious cultural relics, and reflecting the essence of ancient ChineseRead more
Ancient Capitals
Historic Towns and Villages
Religious and Cultural Sites
Cultural and Artistic Centers
Minority Cultural Areas
- Guizhou Province:Home to many ethnic minorities such as the Miao and Dong ethnic groups, where tourists can visit ethnic villages, experience unique ethnic cultures, such as traditional costumes, handicrafts, and folk festivals2.

景点 贵州西江千户苗寨
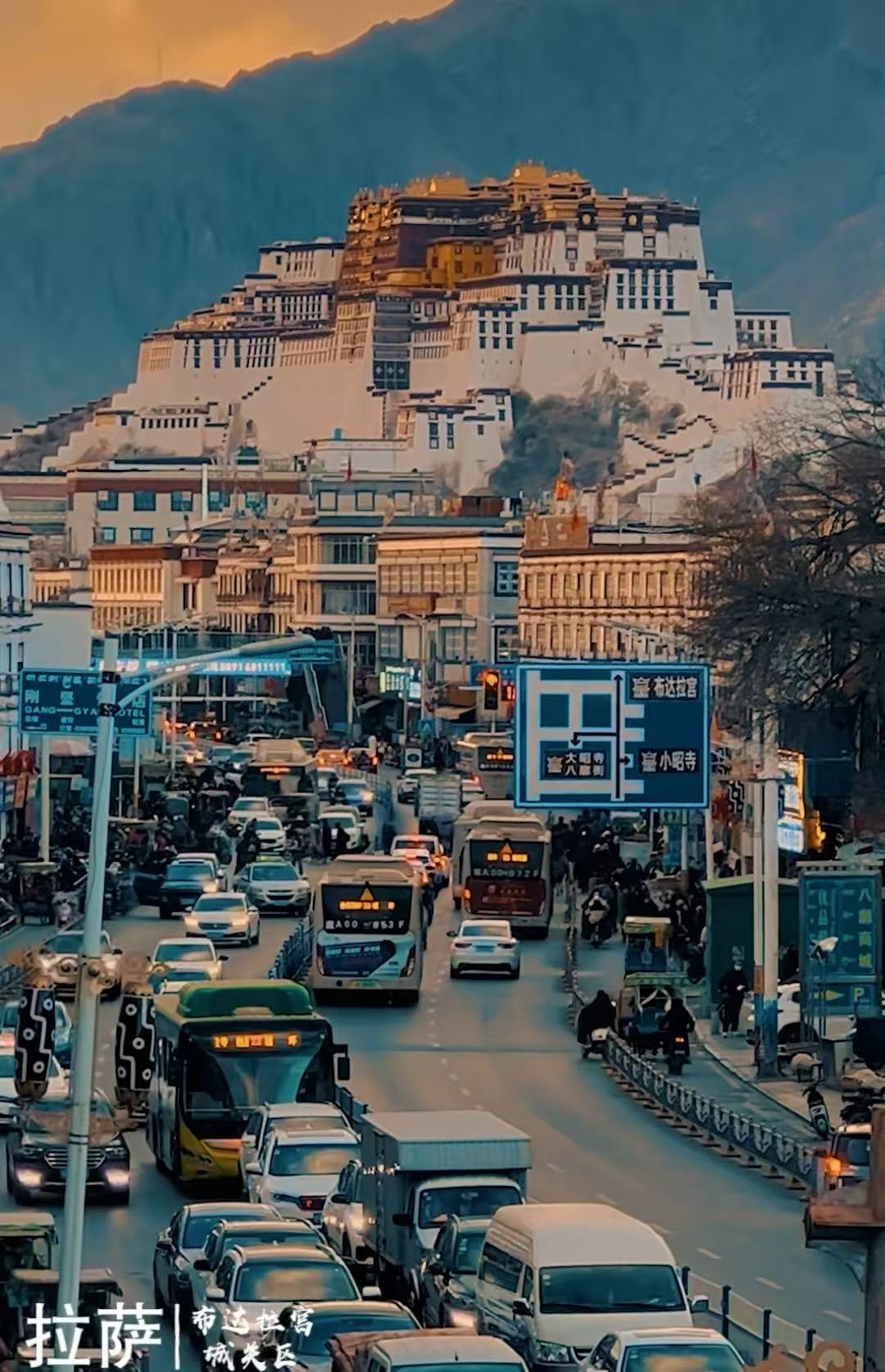
- Tibet Autonomous Region:With unique Tibetan culture, the Potala Palace is a symbol of Tibetan Buddhism, and tourists can also visit monasteries, taste Tibetan food, and experience the unique charm of Tibetan culture2.

See lessWho were the Literati during Confucius' time?
During Confucius' time, the Literati referred to a group of scholars and intellectuals who were well - versed in ancient cultural knowledge, rituals, music, and other aspects. Some of the notable Literati of that era included: Zi Gong: His real name was 端木赐. He was one of Confucius' prominentRead more
How will China's technological innovation drive globaleconomic growth?
China's technological innovation drives global economic growth through multiple channels, mainly in the following aspects1: Infrastructure Construction: High - speed Rail Technology: China has a high - speed rail network with an operating mileage of 38, 000 kilometers, leading the world. TechRead more
- Infrastructure Construction:
- High – speed Rail Technology: China has a high – speed rail network with an operating mileage of 38, 000 kilometers, leading the world. Technologies such as the Fuxing bullet train have not only improved the efficiency of domestic transportation but also promoted the upgrading of the global rail transit industry. For example, the China – Laos Railway and the Jakarta – Bandung High – speed Railway have become models of international cooperation. The World Bank study shows that China’s high – speed rail technology can reduce the construction cost of overseas projects by 40%, providing a feasible plan for the infrastructure modernization of developing countries.
- Digital Economy:
- Mobile Payment: With a mobile payment penetration rate of 86%, China has cultivated a digital ecosystem worth $40 trillion. The technical frameworks of Alipay and WeChat Pay have been borrowed by more than 50 countries. They have helped Indonesia build its local e – wallet DANA, making the cashless transaction volume in Southeast Asia increase by 320% in three years.
- E – commerce Platforms: Through the “Digital Silk Road” initiative, Chinese e – commerce platforms have helped Rwandan coffee farmers sell their products directly to Chinese consumers at a 300% price premium, creating a poverty – alleviation model. The report of the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development shows that China’s digital solutions save more than $12 billion in business costs for developing countries every year.
- Green Technology:
- Photovoltaic Industry: China’s photovoltaic industry contributes 70% of the global module production capacity, reducing the cost of solar power generation by 90% in ten years. The silicon heterojunction battery efficiency developed by LONGi Green Energy has broken through 26.8%. This technology, when implemented in the Red Sea New City project in Saudi Arabia, will build the world’s largest off – grid energy storage system.
- New Energy Vehicles: China’s new energy vehicle exports have increased by 470% in three years, driving Malaysia to establish the first electric vehicle complete industrial chain park in ASEAN. According to the data of the International Energy Agency, China’s clean technology exports reduce global carbon emissions by about 2.8 billion tons per year, equivalent to the annual emissions of the entire European Union.
- Promoting the Upgrading of Global Industrial Chains:
- High – end Manufacturing: In fields such as aerospace and integrated circuits, China has made many technological breakthroughs, continuously improving product quality and production efficiency. These breakthroughs have promoted the transformation and upgrading of related industries worldwide, enabling global industrial chains to move towards the high – end.
- 5G Technology: China is in a leading position in 5G technology. The wide application of 5G has promoted the development of the Internet of Things, smart manufacturing, and other industries, improving the overall operational efficiency of global industries. For example, some factories in Europe and the United States have introduced 5G – enabled smart manufacturing solutions, which have improved production efficiency and product quality.
- International Cooperation and Knowledge Sharing:
- Open Innovation: China is committed to open innovation, sharing its technological achievements and experience with the world. For example, the cross – border payment pilot of the digital yuan and the construction of the “Belt and Road” joint laboratories provide new opportunities and technical support for the economic development of countries along the line.
- International Patent Applications: In 2023, China’s PCT international patent applications accounted for 34.7% of the global total, and the invention patents in the core industries of the digital economy accounted for more than 73%. These patents have promoted the development of related industries worldwide and provided new technical means for solving global economic and social problems.
See less